3 Geospatial Data
3.3 Spatial data have spatial reference
- coordinate values (e.g. XY, XYZ)
- a system of reference for these coordinates (e.g. WGS84)
All spatial data consist of positional information, answering the question ‘where is it?’.
In many applications these will be extended by attributes, answering the question ‘what is where?’
3.4 Spatial data models
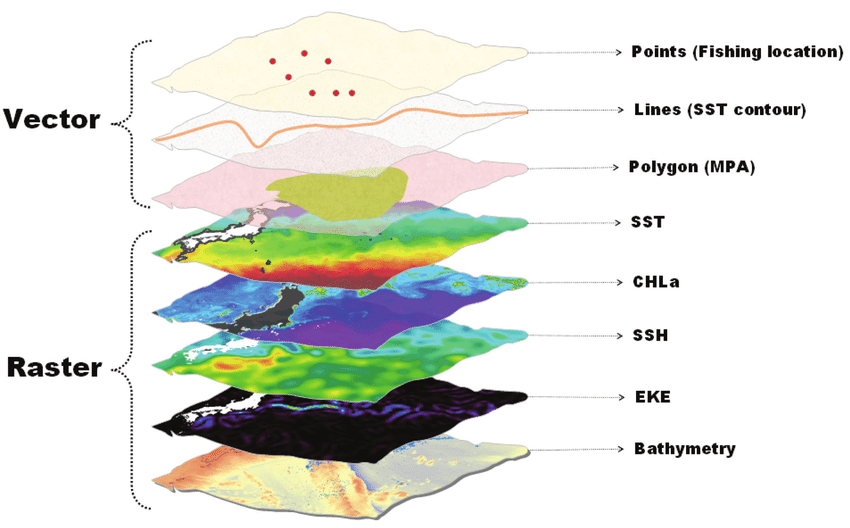
- Point: a single point location, such as a GPS reading or a geocoded address
- Line: a set of ordered points, connected by straight line segments
- Polygon: an area, marked by one or more enclosing lines, possibly containing holes, with no lines intersecting
- Grid: a collection of points or rectangular cells, organised in a regular lattice
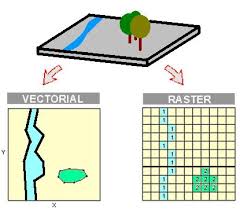
Vector data models
Raster data model